Bacteria in motion
In a joint effort with various international institutions, researchers from the University of Innsbruck have described the movement patterns of the bacterium Escherichia coli. To do so, they used an engineered bacterial strain, experiments under the microscope and complicated functions.

Compression may cool
An international research team from Innsbruck and Geneva has developed a new thermometry method to measure temperatures for low-dimensional quantum gases. With this method it was found that compressing a gas may lead to cooling. The results on this counterintuitive phenomenon have just been published in the prestigious journal Science Advances.
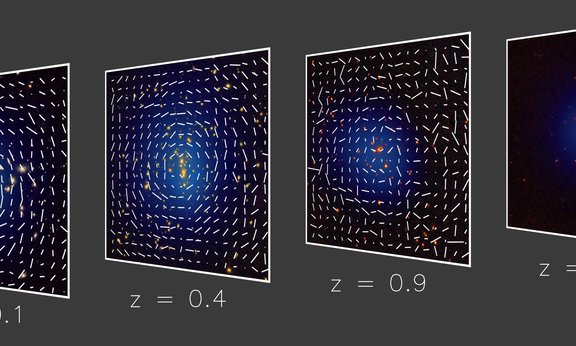
Weighing Galaxy Clusters
Scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics have published the cosmological results of the first X-ray sky survey of the Western Galactic Hemisphere by the eRosita space telescope. The working group for Extragalactic Astrophysics at the University of Innsbruck was also significantly involved in the calculations. The results provide new insights into dark energy, the nature of the Universe and confirm a rejected hypothesis of Albert Einstein.
The “superradiance” revisited
Theoretical physicist Farokh Mivehvar has investigated the interaction of two collections of atoms emitting light inside a quantum cavity – an optical device consisting of two high quality, tiny mirrors facing each other that confines the light within a small area for an extended time. The model and predictions can be implemented and observed in state-of-the-art cavity/waveguide-quantum-electrodynamics experiments and might have applications in the new generation of so-called “superradiant lasers”.

Biomarkers of Aging
A new study proposes a framework to standardize biomarkers of aging and accelerate clinical use. Co-author Chiara Herzog from the European Translational Oncology Prevention and Screening Institute at the University of Innsbruck explains how this could improve the life expectancy and health of the population.

Successful Laser Cooling of Positronium
An international team of scientist including Giovanni Cerchiari from the University of Innsbruck demonstrated laser cooling of positronium, a matter-antimatter system composed of an electron and a positron, which is the antimatter counterpart. This milestone marks a pivotal advancement in our understanding and manipulation of antimatter establishing a foundation for forthcoming experiments and technological advancements.

US ski industry suffered a $5 billion hit from climate change
For the first time, a study has estimated the economic damage of climate change to the ski industry. The study by the University of Innsbruck and the University of Waterloo in Canada reveals that the economic losses to the US ski industry from human-caused climate change exceeded more than US$5 billion over the last two decades.
Network of quantum sensors boosts precision
Quantum sensor technology promises even more precise measurements of physical quantities. A team led by Christian Roos at the University of Innsbruck has now compared the signals of up to 91 quantum sensors with each other and thus successfully eliminated the noise caused by interactions with the environment. Correlation spectroscopy can be used to increase the precision of sensor networks.
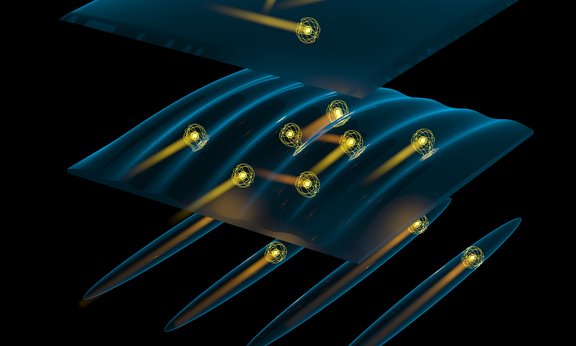
Dimensionality Revealed
An international research team from Innsbruck and Geneva has, for the first time, probed the dimensional crossover for ultracold quantum matter. In the regime between one and two dimensions, the quantum particles perceive their world as being 1D or 2D depending on the length scale on which they are probed: On short distances, their world is 1D, but it is 2D on long distances. The results obtained from correlation measurements have just been published in Nature Physics.

Nano-Oscillator Hits Record Quality Factor
In their latest study, a team led by Tracy Northup at the Department of Experimental Physics unveils the successful creation of a levitated nanomechanical oscillator with an ultra-high quality factor, significantly surpassing previous experimental achievements.
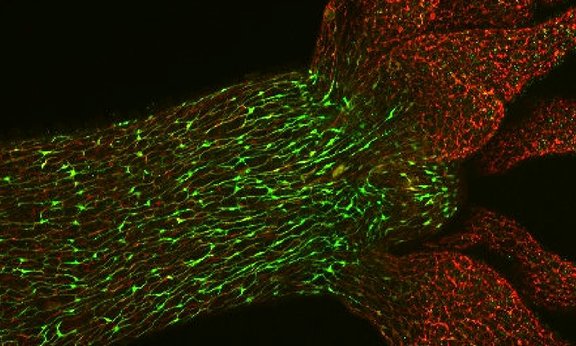
Nerve cells in colour
A novel antibody colors all nerve cells in the model organism Hydra: Scientists were able to observe astonishing details of neuronal stimulus transmission in the nerve network of the freshwater polyp. Bert Hobmayer and his team from the Institute of Zoology contributed to the recently published findings, which are relevant for neurobiology and developmental biology.

Climate Crisis Threatens Alpine Ecosystems
Mountains are particularly affected by climate change: they are warming faster than the lowlands. As the temperature rises, the snow cover is reduced and dwarf shrubs are spreading to higher altitudes - with a strong impact on the seasonal processes of sensitive Alpine ecosystems. This is shown by a new study involving Innsbruck ecologist Michael Bahn, who has carried out field studies over several years in the rear Ötztal valley in Tyrol.

The origin of Cosmic Rays
New results from Gamma-ray astronomy contrast the decade-old standard paradigm for the origin of Galactic cosmic rays. Investigations based on observations with NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope were led by an Innsbruck researcher.

Biodiversity: climate to become main driver
The most comprehensive look to date into the past and future of global biodiversity is provided by a recent study in the journal Science: intensive land use reduced biodiversity by up to around 10 per cent over the course of the 20th century. By 2050, the climate crisis could become the main driver of further biodiversity loss alongside land use. Lauren Talluto from the Department of Ecology at the University of Innsbruck is part of the international team of authors.
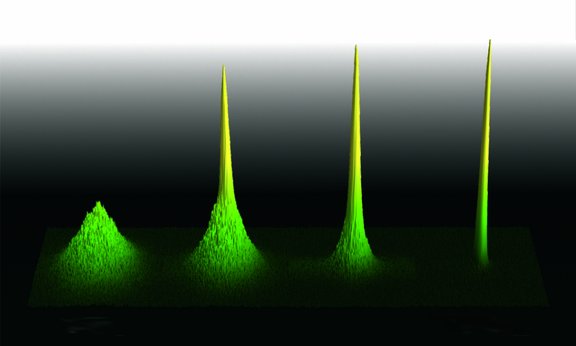
First condensation of non-ground state Cesium atoms
In a pioneering effort, researchers from the University of Innsbruck in collaboration with the University of Durham have for the first time achieved Bose-Einstein condensation of non-ground state cesium atoms. Published in Nature Communications, this research paves the way for new experiments with ultracold atomic gases and the study of many-body quantum physics.

How AI helps programming a quantum computer
Researchers from the University of Innsbruck have unveiled a novel method to prepare quantum operations on a given quantum computer, using a machine learning generative model to find the appropriate sequence of quantum gates to execute a quantum operation. The study, recently published in Nature Machine Intelligence, marks a significant step forward in unleashing the full extent of quantum computing.
