
Building Connections and Knowledge
The fourth Innsbruck-Munich Empirical Economics Workshop took place in late September, set at the scenic location of Maria Waldrast. Organized by Prof. Andreas Steinmayr (University of Innsbruck, Public Finance) and Prof. Joachim Winter (LMU Munich, Economics), this annual event provides junior researchers from both universities with a valuable platform to present their latest work and gain constructive insights from peers and senior colleagues alike.

Clinical Pharmacy Department: Member and Leader of the PCNE
In June 2024, Dr. Ivana Tadic was elected as president of the Pharmaceutical Care Network Europe (PCNE) board, and the Department of Clinical Pharmacy, under the leadership of Univ.-Prof. Dr. Anita Weidmann became the PCNE institutional member.

Philippines in the focus of migration research
Over one million Filipinos leave their country every year to work. The high emigration figures not only concern the Philippine state, but also the economist Andreas Steinmayr. In July 2024, he resumed a long-standing collaboration with the Philippine Department of Immigration, providing researchers with valuable insights into migration dynamics.

Research Integrity Office established
In October 2024, the University of Innsbruck established the Office for Research Integrity. The new unit, which reports directly to Rector Veronika Sexl, combines the agendas of good scientific practice and of the office of the Advisory Board for Ethical Issues in Scientific Research and is headed by Robert Rebitsch.

One-time Cooperation Decisions Unaffected by Increased Benefits to Society
Until now, it was considered certain that people are more likely to cooperate if the benefits from cooperation are higher. A recently published, large-scale study involving researchers from Innsbruck has now called this finding into question: in over 2000 study participants, the researchers found no relationship between benefits from cooperation and willingness to cooperate.

Global Network of Deans of Education meets in Innsbruck
The first in-person meeting of the Global Network of Deans of Education took place at Innsbruck University from 2 to 4 September 2024. About 40 representatives of Networks of Deans of Education and Teacher Associations from the US, Singapore, Canada, Africa, Australia, Jamaica, the UK, Scotland, Germany, Austria, and many more came together to share knowledge and experience addressing the pressing needs teacher education is currently facing.
New multimodal signature could predict immunotherapy success
An international team of researchers led by Francesca Finotello from the Digital Science Center (DiSC) and Department of Molecular Biology has derived a molecular signature from tumour transcriptomics data that quantifies the main sources of heterogeneity in the tumour microenvironment. This innovative signature, which the researchers call iHet, offers deeper insights into patients’ responses to immunotherapy and could improve cancer treatments.

A new type of collective interference effect
A team led by Robert Keil and Tommaso Faleo from the Department of Experimental Physics has investigated the relationship between entanglement and interference in quantum systems of more than two particles in the laboratory. Together with researchers from the University of Freiburg, Germany, and Heriot-Watt University, UK, they gained new insights into the behavior of multi-particle quantum systems. In the interview, Tommaso Faleo explains how interference patterns of more than two photons can be interpreted.

Supercomputer and quantum computer in harmony
Working together, the University of Innsbruck and the spin-off AQT have integrated a quantum computer into a high-performance computing (HPC) environment for the first time in Austria. This hybrid infrastructure of supercomputer and quantum computer can now be used to solve complex problems in various fields such as chemistry, materials science or optimization.

Donations: Higher Returns When Asking for Units of Relief Supplies Rather Than Money
Small changes in how potential donors are approached can achieve significantly higher donation returns than traditional requests for monetary donations. This is the result of an online study conducted by behavioral economists from the universities of Heidelberg, Innsbruck, and Kassel. In the study, potential donors were asked if they wanted to donate relief supplies at a specified unit price and, if so, how many. Using this approach can significantly boost donation income, provided the unit is chosen right.

1,500-year-old reliquary discovered
Since the summer of 2016, archaeologists from Innsbruck have been carrying out excavations in a late antique hilltop settlement in the municipality of Irschen in southern Austria. Two years ago, they made a sensational discovery: a Christian reliquary was still hidden in a previously unknown church. It contained a richly decorated ancient reliquary box made of ivory.

Innsbrucker Digitalexperte in Weltethikkommission berufen
Welche Regeln braucht das Quantenzeitalter – und wie sichern wir Fortschritt für alle? Die Generalsekretärin der UNO-Bildungs- und Wissenschaftsorganisation UNESCO hat Prof. Matthias C. Kettemann vom Institut für Theorie und Zukunft des Rechts als einen von 18 Expert:innen der Weltkommission für Wissenschafts- und Technologieethik berufen.

France is the statistical favourite for the EURO 2024
The French national team is the favourite for the upcoming 2024 European Football Championships, while England and Germany also have high hopes of winning the title, according to experts from the Universities of Innsbruck and Luxembourg, Molden University of Applied Sciences and the Technical Universities of Dortmund and Munich.

New biomarker predicts success of immunotherapy in kidney cancer
Immunotherapy increases survival rates in kidney cancer, but does not work for everyone. A Leuven research team developed a new method to predict which patients will benefit from it. The team of Francesca Finotello (Computational Biomedicine Group) from the University of Innsbruck also contributed. Their study, published in the journal Nature Medicine, also opens new avenues to even more effective treatments.

Euclid finds thousands of new galaxies
After being launched last summer, ESA's Euclid space telescope has already been delivering data for almost a year. The first scientific results are being published today. They show that the new instrument is capable of detecting a representative sample of all galaxies in the universe. For example, a study led by the University of Innsbruck was able to identify over 600 previously unknown dwarf galaxies in the Perseus galaxy cluster.

How AI helps programming a quantum computer
Researchers from the University of Innsbruck have unveiled a novel method to prepare quantum operations on a given quantum computer, using a machine learning generative model to find the appropriate sequence of quantum gates to execute a quantum operation. The study, recently published in Nature Machine Intelligence, marks a significant step forward in unleashing the full extent of quantum computing.

Hannes Pichler received Ignaz L. Lieben Prize
In May Hannes Pichler has been awarded the Ignaz L. Lieben Prize in Vienna for his groundbreaking work in the field of quantum many-body physics and quantum information science. This oldest research prize of the Austrian Academy of Sciences (ÖAW) is endowed with 36,000 US dollars.

Natalia Piórecka wins New European Bauhaus Prize
Natalia Piórecka, Senior Scientist at Integrative Design / Extremes at the Institute of Experimental Architecture at the University of Innsbruck, has been awarded the prestigious New European Bauhaus Prize for her project UrbanMYCOskin.

Biodiversity: climate to become main driver
The most comprehensive look to date into the past and future of global biodiversity is provided by a recent study in the journal Science: intensive land use reduced biodiversity by up to around 10 per cent over the course of the 20th century. By 2050, the climate crisis could become the main driver of further biodiversity loss alongside land use. Lauren Talluto from the Department of Ecology at the University of Innsbruck is part of the international team of authors.

Education for Sustainable Development (ESD)
From 3 to 5 April 2024, a Peer Learning Activity (PLA) developed by the Rectorate, the Aurora European University Office Innsbruck and UniNEtZ took place on the topic of "Education for Sustainable Development (ESD)".

Climate Crisis Threatens Alpine Ecosystems
Mountains are particularly affected by climate change: they are warming faster than the lowlands. As the temperature rises, the snow cover is reduced and dwarf shrubs are spreading to higher altitudes - with a strong impact on the seasonal processes of sensitive Alpine ecosystems. This is shown by a new study involving Innsbruck ecologist Michael Bahn, who has carried out field studies over several years in the rear Ötztal valley in Tyrol.

The origin of Cosmic Rays
New results from Gamma-ray astronomy contrast the decade-old standard paradigm for the origin of Galactic cosmic rays. Investigations based on observations with NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope were led by an Innsbruck researcher.
Dimensionality Revealed
An international research team from Innsbruck and Geneva has, for the first time, probed the dimensional crossover for ultracold quantum matter. In the regime between one and two dimensions, the quantum particles perceive their world as being 1D or 2D depending on the length scale on which they are probed: On short distances, their world is 1D, but it is 2D on long distances. The results obtained from correlation measurements have just been published in Nature Physics.
Mastodon for all university employees
The communications team at the University of Innsbruck is further expanding the use of the non-profit and data protection-friendly microblogging service Mastodon and is now also opening the service to all of the more than 5,000 employees of the University of Innsbruck following the organizational units. Mastodon has been connected to the university's own login system.
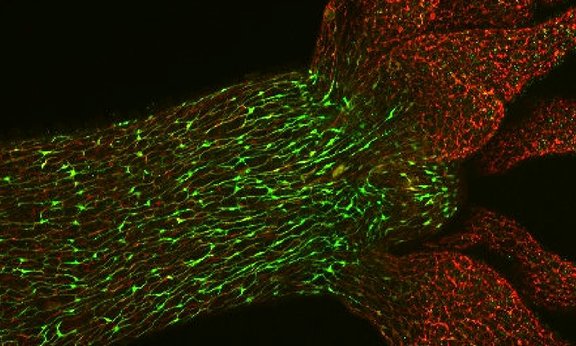
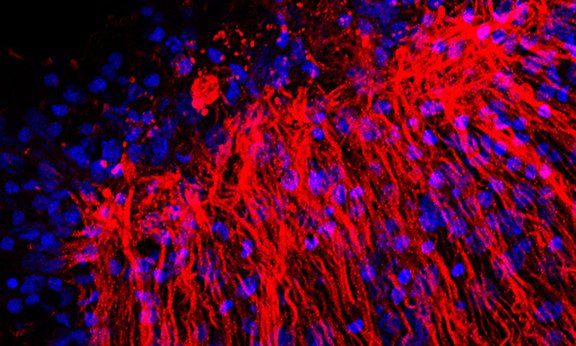
Nerve cells in colour
A novel antibody colors all nerve cells in the model organism Hydra: Scientists were able to observe astonishing details of neuronal stimulus transmission in the nerve network of the freshwater polyp. Bert Hobmayer and his team from the Institute of Zoology contributed to the recently published findings, which are relevant for neurobiology and developmental biology.

Nano-Oscillator Hits Record Quality Factor
In their latest study, a team led by Tracy Northup at the Department of Experimental Physics unveils the successful creation of a levitated nanomechanical oscillator with an ultra-high quality factor, significantly surpassing previous experimental achievements.

Marie Skłodowska-Curie Actions Award for Psychologist
Dr Sofia Amaoui was awarded MSCA funding for her project entitled "Attitudes Towards Intimate Partner Violence against Women: from Neural Networks to Daily Life Experience" as part of the Social Sciences and Humanities (SOC) programme.
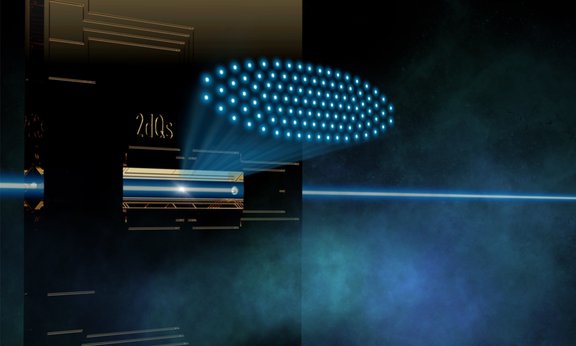
Network of quantum sensors boosts precision
Quantum sensor technology promises even more precise measurements of physical quantities. A team led by Christian Roos at the University of Innsbruck has now compared the signals of up to 91 quantum sensors with each other and thus successfully eliminated the noise caused by interactions with the environment. Correlation spectroscopy can be used to increase the precision of sensor networks.

US ski industry suffered a $5 billion hit from climate change
For the first time, a study has estimated the economic damage of climate change to the ski industry. The study by the University of Innsbruck and the University of Waterloo in Canada reveals that the economic losses to the US ski industry from human-caused climate change exceeded more than US$5 billion over the last two decades.

Book tip: Teaching International Law
In a world characterised by growing international conflicts and existential threats to humanity, international law is becoming increasingly important. The book "Teaching International Law" sheds light on this urgency and offers profound insights into the challenges and opportunities of teaching international law.

Successful Laser Cooling of Positronium
An international team of scientist including Giovanni Cerchiari from the University of Innsbruck demonstrated laser cooling of positronium, a matter-antimatter system composed of an electron and a positron, which is the antimatter counterpart. This milestone marks a pivotal advancement in our understanding and manipulation of antimatter establishing a foundation for forthcoming experiments and technological advancements.

Biomarkers of Aging
A new study proposes a framework to standardize biomarkers of aging and accelerate clinical use. Co-author Chiara Herzog from the European Translational Oncology Prevention and Screening Institute at the University of Innsbruck explains how this could improve the life expectancy and health of the population.
The “superradiance” revisited
Theoretical physicist Farokh Mivehvar has investigated the interaction of two collections of atoms emitting light inside a quantum cavity – an optical device consisting of two high quality, tiny mirrors facing each other that confines the light within a small area for an extended time. The model and predictions can be implemented and observed in state-of-the-art cavity/waveguide-quantum-electrodynamics experiments and might have applications in the new generation of so-called “superradiant lasers”.

Compression may cool
An international research team from Innsbruck and Geneva has developed a new thermometry method to measure temperatures for low-dimensional quantum gases. With this method it was found that compressing a gas may lead to cooling. The results on this counterintuitive phenomenon have just been published in the prestigious journal Science Advances.
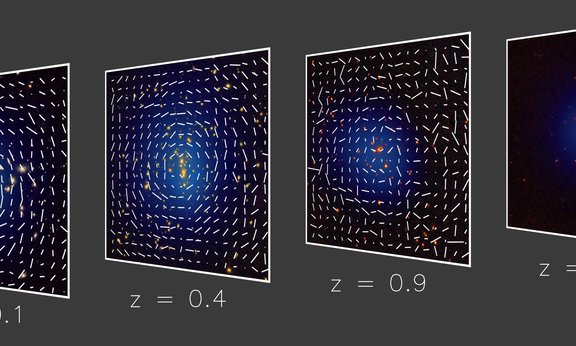
Weighing Galaxy Clusters
Scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics have published the cosmological results of the first X-ray sky survey of the Western Galactic Hemisphere by the eRosita space telescope. The working group for Extragalactic Astrophysics at the University of Innsbruck was also significantly involved in the calculations. The results provide new insights into dark energy, the nature of the Universe and confirm a rejected hypothesis of Albert Einstein.

Buchtipp: Rohstoffe – Menschen – Wissen
Band 35 der Reihe „Innsbrucker Historische Studien“, herausgegeben von Elena Taddei und Georg Neuhauser, befasst sich mit der Ressourcengeschichte des historischen Tirols vom Spätmittelalter bis ins 20. Jahrhundert. Vieles fällt dabei unter „Ressourcen“ – von Rohstoffen wie Holz, „Humanressourcen“ wie Söldner bis hin zu Wissensressourcen.
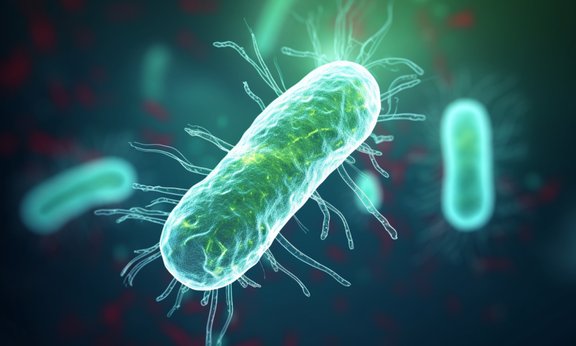
Bacteria in motion
In a joint effort with various international institutions, researchers from the University of Innsbruck have described the movement patterns of the bacterium Escherichia coli. To do so, they used an engineered bacterial strain, experiments under the microscope and complicated functions.

The Secret Diary of Karl Benedikt Hase
Karl Benedikt Hase (1780–1864) is recognised as one of the foremost Greek scholars in the French academia of his time. The LAGOOS project has at its core the discovery of 9 volumes of the private diary of Hase, written in Ancient Greek and preserved at the Goethe- und Schiller-Archiv, Weimar. Specialists of Late Antique and Byzantine history and literature applaud the outstanding value of his work as an editor and commentator. They have also, however, identified him as the perpetrator of a series of forgeries on documents of Byzantine history.

Significant decline of CO2 emissions in Innsbruck
Air monitoring measurements at the University of Innsbruck's atmospheric observatory show that carbon dioxide emissions in western Austria have fallen by around 20 percent since 2018. Emissions are therefore well below the levels predicted by various models. Observational data is becoming increasingly important for assessing greenhouse gas budgets.

Observing macroscopic quantum effects in the dark
Be fast, avoid light, and roll through a curvy ramp: This is the recipe for a pioneering experiment proposed by theoretical physicists in a recent paper published in Physical Review Letters. An object evolving in a potential created through electrostatic or magnetic forces is expected to rapidly and reliably generate a macroscopic quantum superposition state.

Printing inks made from plants
On the path to a circular economy, Judith Deriu is developing natural color pigments from plants and uses them to make sustainable printing inks for industry in the laboratory at the Research Institute of Textile Chemistry and Textile Physics in Dornbirn.

Iodic acid replaces ammonia in aerosol formation
Iodine from the world's oceans forms iodine oxoacids, which can accelerate the formation of sulfuric acid particles in the atmosphere by a factor of 10,000. This was discovered by scientists of the CLOUD experiment with the participation of the University of Innsbruck. The increasing iodine emissions have an impact on the climate that is still under-estimated in current models.
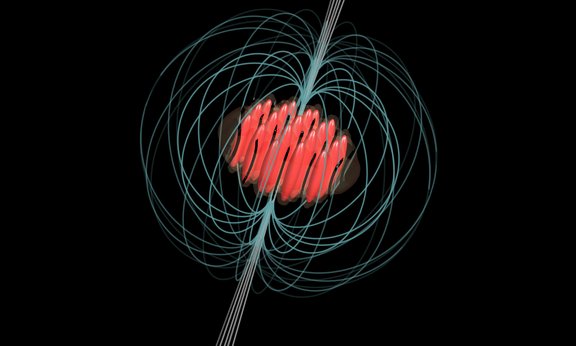
Unlocking Neutron Star Rotation Anomalies
A collaboration between quantum physicists and astrophysicists, led by Francesca Ferlaino and Massimo Mannarelli, has achieved a significant breakthrough in understanding neutron star glitches. They were able to numerically simulate this enigmatic cosmic phenomenon with ultracold dipolar atoms. This research establishes a strong link between quantum mechanics and astrophysics and paves the way for quantum simulation of stellar objects from Earth.

Austria's quantum science is taking off
Yesterday, the FWF Cluster of Excellence for quantum sciences has been officially launched in Innsbruck. As part of the Excellence Initiative, the Clusters of Excellence are Austrian beacons of basic research. Quantum Science Austria (quantA) brings together over 60 research groups in Innsbruck, Vienna, Linz and Klosterneuburg and is intended to strengthen Austria's leading position in quantum science in the long term.

Focus climate communication: Project PEAK launched
The University of Innsbruck is enhancing its science communication in the fields of climate, biodiversity, and sustainability. A key development in this initiative is the creation of a new online platform, designed to showcase the university's extensive scientific expertise. This platform, part of the 'PEAK' project (Perspectives on Engagement, Accountability, and Knowledge), offers insights into current research and includes a growing database of expert profiles.

Quantum tool opens door to uncharted phenomena
Scientists led by Peter Zoller have developed a new tool for the measurement of entanglement in many-body systems and demonstrated it in experiments. The method enables the study of previously inaccessible physical phenomena and could contribute to a better understanding of quantum materials. The work has now been published in Nature.

From Glaciers to Rainfall: Ten Years in the Andes
Scientists at the University of Innsbruck have been studying the water cycle and glaciers in the Andes near Huaraz in northern Peru for a long time. They recently documented a previously unreported rainfall phenomenon. These light rainfalls, known locally as "Pushpa", mark the beginning of the sowing season. Their unpredictability from one year to the next complicates matters for farmers, a situation potentially worsened by climate change.

Sustainability of artificial snow on ski-slopes
Researchers from the Universities of Innsbruck and Waterloo have studied the environmental impact of artificial snowmaking and its effect on the sustainability of ski tourism with Canada as an example. High water and energy consumption and the associated CO2 emissions are a burden on the environmental balance sheet; energy from renewable sources can make winter sports considerably more sustainable.

Ice cliffs as an early warning system for the climate
It is rare to find glaciers bounded on land by vertical ice cliffs. These ice cliffs respond with particular sensitivity to environmental changes. Research teams from Tyrol and Styria are investigating ice formations at a site in the far north of Greenland. The researchers intend to draw conclusions about the development of the Arctic climate based on the changes in the glacier walls.

Interacting polarons
In physics, quasiparticles are used to describe complex processes in solids. In ultracold quantum gases, these quasiparticles can be reproduced and studied. Now, for the first time, Austrian scientists led by Rudolf Grimm have been able to observe in experiments how Fermi polarons – a special type of quasiparticle – can interact with each other. Their findings have been published in Nature Physics.

Deep look into the dipolar quantum world
In a groundbreaking collaboration, two world-leading research groups, one led by Francesca Ferlaino and one by Markus Greiner, have joined force to develop an advanced quantum gas microscope for magnetic quantum matter. This state-of-the-art instrument reveals intricate dipolar quantum phases shaped by the interactions as reported in Nature.

El Niño's Changing Patterns: Human Influence on Natural Variability
Two recent scientific studies led by Dr. Paul Wilcox from the Department of Geology at the University of Innsbruck provide new insights into Earth's climate dynamics, with a particular focus on the El Niño phenomenon. The results show how El Niño responds to natural factors over extended periods, while highlighting the increasing role of human activities in shaping this climatic phenomenon in the modern era.

Staff Week brings Aurora Partner to Innsbruck
Moving more together: This was the motto of the first Aurora Staff Week, which took place at the University of Innsbruck from 2 to 6 October. Participants from academia and administration from Reykjavik to Naples exchanged ideas with colleagues from the University of Innsbruck in order to develop new activities and projects.

Cross-alpine transit protests
When the large highways crossing the Austrian and Swiss Alps were built, citizens’ movements protesting the transalpine traffic started to form in both countries from the 1970s onwards. They found common ground in blaming EU policy but overall employed distinct methods, also with varying success, and never really joined forces. In a recent project, historians in Innsbruck, Basel and Munich made these two environmental initiatives the subject of their comparative research.

Statistics of the invisible
In order to obtain information about dark matter and dark energy from the huge amounts of data to be generated by the new ESA probe Euclid, Innsbruck astrophysicist Laila Linke and her team are using novel statistical methods. As soon as Euclid sends its first data to Earth, the researchers intend to have a tool ready to gain new information on the most important questions concerning the invisible side of the cosmos.

ERC Grant for Biodiversity Research
For his research on the influence of biodiversity on long-term forest dynamics, Rubén D. Manzanedo has been awarded a Starting Grant from the European Research Council (ERC). Currently a researcher at ETH Zurich, Dr. Manzanedo applied for the grant, which is endowed with around 1.5 million euros, through the University of Innsbruck.
Learn modeling and simulation
How to prepare for the third pillar of science - let's call it computing or simulation? How to keep up with the ever-evolving computational tools relevant to one’s field of studies? This winter term, the Extension Programme Scientific Computing (EPSC) is back for its second year, offering 7 lectures on how to approach these challenges for modern scientists and professionals.
RNA-drug interactions
How active compounds affect RNA and thus the expression of genes is of great interest for the development of potential therapeutics. Innsbruck chemists have now used a method they recently developed to study the binding of the aminoglycoside Neomycin B to a so-called mRNA riboswitch.

The carbon cycle is speeding up
Soil is the largest natural carbon storage in the world. In Northern ecosystems particularly large amounts of carbon are stored, but they are also particularly strongly affected by global warming. A recently published study by an international team led by Michael Bahn of the University of Innsbruck investigated how ongoing warming affects the uptake and release of carbon dioxide in subarctic grassland. The researchers used a geothermally active area in Iceland as a natural „climate chamber”.

Rainer Blatt awarded Herbert Walther Prize
During the World of Photonics Congress in Munich, Rainer Blatt was presented with the Herbert Walther Prize 2023. He received the award for his outstanding contributions to quantum optics and quantum information as well as his leading role in advancing this research field.
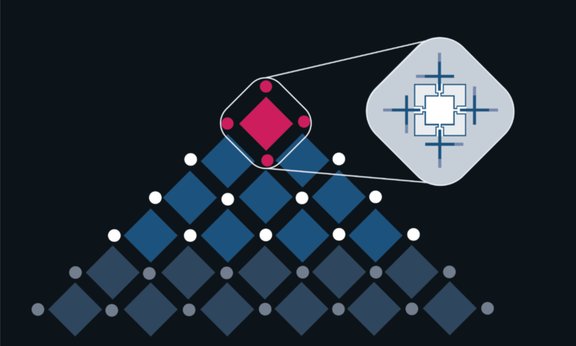
Chip with Austrian quantum architecture operational
The Japanese IT group NEC has built the first quantum processor with the ParityQC architecture. The Parity technology was invented at the University of Innsbruck and is being further refined and marketed by the quantum spin-off ParityQC. NEC is now making the quantum computer, which specializes in optimization problems, available to the scientific community via the cloud.
Negatively charged and yet pretty cold
Anions, negatively charged ions, are reluctant to be cooled. Physicists led by Matthias Weidemüller from Heidelberg University and Roland Wester from the University of Innsbruck have now developed a method for cooling molecular anions to below 3 Kelvin in a remarkably short time. This enables, for example, new investigations of chemical reactions in space.

University of Innsbruck continues its successful path in Aurora Alliance
Cooperation between European universities in teaching, research and administration is at the centre of the European Universities Initiative. Since 2020, the University of Innsbruck has been part of the Aurora Alliance, one of 44 European alliances selected by the European Commission as "Universities of the Future". Over the next four years, the Aurora Alliance will receive around 15 million euros in funding, enabling it to continue developing and implementing innovative cooperation projects.

A new strategy enables molecular diversity
The research group led by chemist Thomas Magauer has accomplsihed a divergent strategy to synthesize nine complex natural compounds. The developed method requires significantly less time and results in a variety of compounds with different structures and biological properties.

Wittgenstein Award for quantum physicist Hans Briegel
Hans J. Briegel, a physicist researching at the intersection of quantum information, machine learning and philosophy, was awarded Austria's highest science prize, the Wittgenstein Prize, on Thursday. Briegel is "one of the most creative researchers in a field in which Austria plays a leading role," said the international jury.

Workshop: “Sustainability in a changing legal order”
As part of the seminar "Sustainability in Constitutional, European and International Law", Prof. Esther Happacher, Prof. Walter Obwexer (both University of Innsbruck) and Prof. Jens Woelk (University of Trento) organised an Open Workshop on "Sustainability in a changing legal order" on 26 May 2023.

Alps: Lightning activity doubled in a few decades
In the high altitudes of the European Eastern Alps, the number of detected lightning strikes has doubled in the course of the last 40 years. Causes for this are to be found in the effects of the climate crisis. A team of Innsbruck researchers from the Departments of Geosciences, Atmospheric Sciences and Statistics has now published their findings in the journal Climate Dynamics.

Morality and competition in science
How does competition influence moral behaviour? Studies have so far found evidence for both a negative and a positive influence of competition on moral behaviour. Researchers from Innsbruck, Vienna, Stockholm and Amsterdam are using this unanswered question in a meta-study to investigate the extent to which different study designs can be responsible for variability in scientific results. The study was recently published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).

Quantum matter: Tuning density waves
Scientists from the University of Innsbruck, together with colleagues from the EPFL, have found a new way to create a crystalline structure emerging as a “coherent matter density wave” in an atomic gas. The findings help to better understand the intriguing behavior of quantum matter close to absolute zero temperature.
Boost for the quantum internet
A quarter of a century ago, theoretical physicists at the University of Innsbruck made the first proposal on how to transmit quantum information via quantum repeaters over long distances which would open the door to the construction of a worldwide quantum information network. Now, a new generation of Innsbruck researchers has built a quantum repeater node for the standard wavelength of telecommunication networks and transmitted quantum information over tens of kilometers.

Natural product synthesized from coral
Chemists led by Thomas Magauer at the University of Innsbruck succeeded in synthesizing the natural product Waixenicin A for the first time. This molecule is found in soft corals and is of great interest to the pharmaceutical industry due to its potential medical applications.

High-alpine animal species need more protected areas
Melting glaciers due to global warming caused by the climate crisis have massive consequences for biodiversity in the Alpine region, as an international team of researchers including the Innsbruck ecologist Leopold Füreder has now shown for the first time for a period between 2020 and 2100. According to the study, numerous invertebrate species are threatened with the loss of their habitats. The researchers call for the expansion of protected areas, also in glacier forelands. The study has been published in Nature Ecology & Evolution.

Great Basin: History of water supply in one of the driest regions in the USA
An international team including Simon Steidle from the Quaternary Research Group at the Department of Geology at the University of Innsbruck has reconstructed the evolution of groundwater in the Great Basin, USA – one of the driest regions on Earth – up to 350,000 years into the past with unprecedented accuracy. The results shed new light on the effects of climate change on water supply and provide important insights for the sustainable use of groundwater resources. The study was published in the journal Nature Communications Earth & Environment.

Quantum computer in reverse gear
Large numbers can only be factorized with a great deal of computational effort. Physicists at the University of Innsbruck, Austria, led by Wolfgang Lechner are now providing a blueprint for a new type of quantum computer to solve the factorization problem, which is a cornerstone of modern cryptography.
Two qudits fully entangled
Recently quantum computers started to work with more than just the zeros and ones we know from classical computers. Now a team at the University of Innsbruck, Austria, demonstrates a way to efficiently create entanglement of such high-dimensional systems to enable more powerful calculations.

EU Flagship project Millenion launched
The Millenion project focuses on modular scalability and accessibility aspects of trapped-ion quantum computers, tackling the transition from current laboratory-based experiments to industry-grade quantum computing technologies. 14 academic and industrial leaders across Europe are joining forces to deliver a modular and scalable quantum computing suite with high performance cluster integration and a fault-tolerant register of up to 1000 qubits.
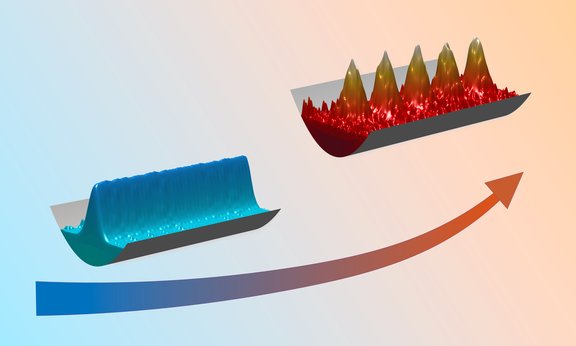
Quantum liquid becomes solid when heated
Solids can be melted by heating, but in the quantum world it can also be the other way around: In a joint effort, an experimental team led by Francesca Ferlaino in Innsbruck, Austria, and a theoretical team led by Thomas Pohl in Aarhus, Denmark, show in Nature Communications how a quantum liquid forms supersolid structures by heating. The scientists obtained a first phase diagram for a supersolid at finite temperature.

Best Paper Award for Adam Jatowt
Computer scientist Adam Jatowt was awarded the Best Paper Award at the European Conference on Information Retrieval (ECIR) this year in Dublin for the article "Temporal Natural Language Inference: Evidence-Based Evaluation of Temporal Text Validity".

Collaboratively exploring vital calcium channels
Innsbruck is an internationally renowned center for voltage gated calcium channel research. A new generation of scientists at the University of Innsbruck and the Medical University Innsbruck continues this successful path. Based on the FWF-funded doctoral program CavX, the researchers are investigating together a wide range of calcium channel properties and functions in health and disease using the most state-of-the-art methods.

Turbulence: Decades-old theory gets a major remake
Turbulence plays an essential role in weather and climate, and correctly representing its effects in numerical models is crucial for accurate weather forecasts and climate projections. However, the theory describing the effect of turbulence has not changed since its conception in 1950s, despite the fact that it is not representative for the majority of the Earth’s land surface, especially over mountains and polar regions. The Innsbruck meteorologist Ivana Stiperski has now extended the turbulence theory to complex atmospheric conditions. The researcher thus paves the way for the first generalized turbulence theory over complex terrain.

Three Clusters of Excellence in Innsbruck
With highly endowed clusters of excellence, the Austrian Science Fund FWF creates Austrian flagships of basic research. The University of Innsbruck will coordinate the Cluster of Excellence for Quantum Sciences and is involved in two Clusters of Excellence on political, social and cultural developments in Eurasia and on materials for energy conversion and storage.

Quantum Chemistry: Molecules caught tunneling
Physicists led by Roland Wester of the University of Innsbruck have now for the first time observed a quantum mechanical tunneling reaction in experiments. The observation can also be described exactly in theory. With the study published in Nature, the scientists provide an important reference for this fundamental effect in chemistry. It is the slowest reaction with charged particles ever observed.

High-performance computer with quantum coprocessor
With 9 million euros in funding from the NextGenerationEU recovery plan for Europe, the University of Innsbruck will combine a quantum computer with a supercomputer in the coming months. The novel system will be used in various fields such as computer science, physics, mathematics and beyond and will be open to all scientists in Austria for research and teaching.

Tracing the origin of life
A team of scientists from France and Austria has discovered a new abiotic pathway for the formation of peptide chains from amino acids - a key chemical step in the origin of life. The current study provides strong evidence that this crucial step for the emergence of life can indeed occur even in the very inhospitable conditions of space.

Entangled atoms across the Innsbruck quantum network
Trapped ions have previously only been entangled in one and the same laboratory. Now, teams led by Tracy Northup and Ben Lanyon from the University of Innsbruck have entangled two ions over a distance of 230 meters. The experiment shows that trapped ions are a promising platform for future quantum networks that span cities and eventually continents.
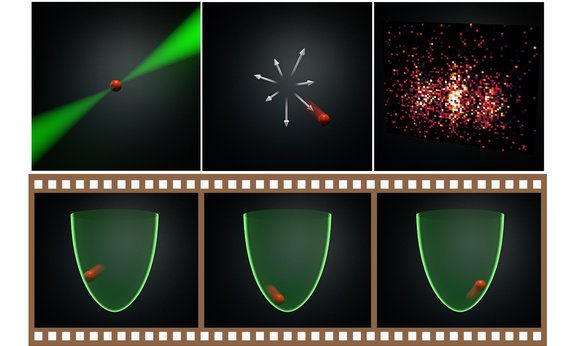
A Quantum Video Reel
When it comes to creating ever more intriguing quantum systems, a constant need is finding new ways to observe them in a wide range of physical scenarios. JILA Fellow Cindy Regal and JILA and NIST Fellow Ana Maria Rey have teamed up with Oriol Romero-Isart from the University of Innsbruck and IQOQI to show that a trapped particle in the form of an atom readily reveals its full quantum state with quite simple ingredients, opening up opportunities for studies of the quantum state of ever larger particles.

Underlying assumptions of air quality need to be redefined
Long-term measurements in the urban area of Innsbruck, Austria, show that the fraction of ozone near the surface tends to be overestimated in atmospheric models. Consequently, a fundamental assumption for air quality forecasting has to be reinterpreted for urban areas. Measurements by an international team led by atmospheric scientist Thomas Karl of the University of Innsbruck also show that direct nitrogen dioxide emissions are overestimated.

Blast Chiller for the Quantum World
The quantum nature of objects visible to the naked eye is currently a much-discussed research question. A team led by Innsbruck physicist Gerhard Kirchmair has now demonstrated a new method in the laboratory that could make the quantum properties of macroscopic objects more accessible than before. With the method, the researchers were able to increase the efficiency of an established cooling method by an order of a magnitude.

Quantum entanglement sharpens measurements
According to Heisenberg's uncertainty principle, two complementary properties, for example single components of a magnetic field, cannot be determined with arbitrary precision at the same time. An international team of scientists has now tested a new method on about a dozen quantum computers with which multiple parameters can be optimally determined simultaneously using entangled copies of a quantum state.

International experts introduce new master's degree in pharmacy
Since the winter semester 2022/23, the University of Innsbruck and the Medical University of Innsbruck offer the joint master's programme "Pharmaceutical Sciences". International experts from industry and regulatory authorities were guests at the kick-off.

Digital information platform for refugees
At the International Conference on Information Systems ICIS 2022 in Copenhagen, Maximilian Schreieck from the Department of Information Systems, Production Management and Logistics has been awarded the AIS Impact Award for his support of digital solutions for refugees.

Heat and cold as health hazards
Both hot and cold environments trigger a stress response in the human body and can lead to cardiovascular problems. Physiologist Justin Lawley from the Department of Sport Science and colleagues have recently investigated both factors in scientific studies. The results, which were published in the Journals Scientific Reports and Experimental Physiology, are especially interesting in light of the current multiple global crises.

Leveraging Ethics to Make Quantum Research Sustainable
Innsbruck is a leading center in the development of new quantum technologies. In order to understand the processes of societal change triggered by these technologies and to be able to develop corresponding ethics frameworks, the University of Innsbruck is founding today the Innsbruck Quantum Ethics Lab (IQEL), in which experts from various disciplines will work together.

Statistics: Brazil is the clear favourite going into the FIFA World Cup
After being eliminated in the quarter-finals four years ago, the Brazilian national team is once again the clear favourite to win the FIFA World Cup. But Argentina, the Netherlands, Germany and France also have a good chance of winning the title – as shown by an international team of researchers from the Universities of Innsbruck, Ghent and Luxembourg and the Technical Universities of Dortmund and Munich.
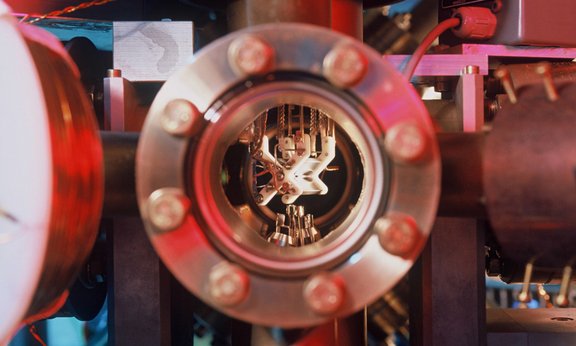
Method to characterize large quantum computers
Quantum devices are becoming ever more complex and powerful. Researchers at the University of Innsbruck, in collaboration with the Johannes Kepler University Linz and the University of Technology Sydney, are now presenting a method to characterize even large quantum computers using only a single measurement setting.
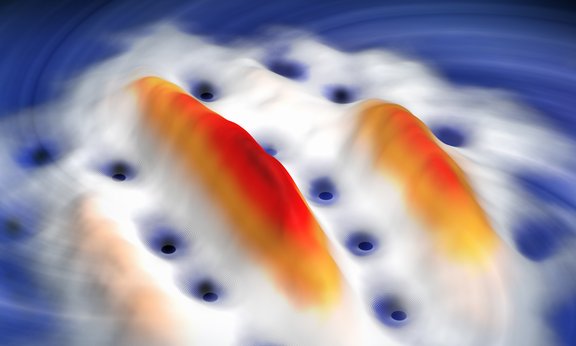
Ultra-cold mini twisters
A team of quantum physicists from Innsbruck, Austria, led by three-time ERC laureate Francesca Ferlaino has established a new method to observe vortices in dipolar quantum gases. These quantum vortices are considered a strong indication of superfluidity, the frictionless flow of a quantum gas, and have now been experimentally detected for the first time in dipolar gases.

New form of universal quantum computers
Computing power of quantum machines is currently still very low. Increasing it is still proving to be a major challenge. Physicists at the University of Innsbruck now present a new architecture for a universal quantum computer that overcomes such limitations and could be the basis of the next generation of quantum computers soon.

Build an advanced European quantum internet ecosystem
The Quantum Internet Alliance has started a seven-year program to build an innovative Quantum Internet ecosystem in Europe. The first phase has a budget of 24 million euros. The research groups led by Tracy Northup and Benjamin Lanyon at the Department of Experimental Physics of the University of Innsbruck and the quantum computer spin-off AQT will be involved in the project.

Prominent researchers’ work gets published more easily
Research work by renowned researchers is rated significantly better than work by lesser-known researchers, despite the same quality. This was the conclusion reached by a team of researchers led by Jürgen Huber from the Department of Banking and Finance in a recently published study. The collaboration of Vernon Smith, winner of the 2002 Nobel Prize in Economics, was crucial to the success of the study.

Migration as morality politics
Migration often serves as an arena for conflicting values. In this context, religious groups, civil society organisations and local authorities often show a more liberal attitude than the state. The political scientist Julia Mourão Permoser applies a new analytical approach to this as yet unexplored aspect.

COVID-19: The current semester
Even though Corona will remain and we will all have to live with it in the long run, we are currently in a very good situation - from the point of view of society as a whole as well as within the university. Therefore, all currently valid regulations at the University of Innsbruck regarding COVID-19 will be lifted with immediate effect. The Rector's team is very concerned about the health of all university employees, which is why the situation around COVID-19 will be monitored in the future in order to be able to take necessary steps if necessary.

IMC 2022: 800 mountain researchers met in Innsbruck
From 11 to 15 September, the University of Innsbruck hosted the second International Mountain Conference, the world's largest conference exclusively on mountain issues. Over the course of four days, numerous experts from a wide range of disciplines engaged in an interdisciplinary exchange on various aspects of mountain research. The organizers Wolfgang Gurgiser and Stefan Mayr from the University of Innsbruck’s Research Area "Mountain regions" sum up the conference positively and are considering a next edition of the IMC in 2025.

Reading old handwriting with Transkribus
Using artificial intelligence, computers can decipher handwritten texts and make them readable for everyone. The Transkribus platform, co-developed at the University of Innsbruck, Austria, makes this technology available to scholars and the general public. An ever-growing group of people are using Transkribus to research their family history. On 29 and 30 September 2022, users from all over the world are going to meet in Innsbruck.

Hannes Pichler wins New Horizons in Physics Prize
Quantum physicist Hannes Pichler receives a highly endowed research prize. He will be awarded a New Horizons Prize in Physics at the Breakthrough Prize Awards Ceremony. The $100,000 award is given to early-career scientists who have already made a significant impact on their field.

The ELI-Hub Award 2022 goes to Austria
The Austrian Hub is delighted about receiving the Annual Hub Award of the European Law Institute. With this prize, the ELI honours a Hub every year that has made a special contribution to the goals of the European Law Institute.

Climate change threatens ice caves in Austria
Eight ice caves in four Austrian federal states: A team of geologists from the University of Innsbruck has comprehensively documented the loss and gain of ice in Alpine ice caves over the last 2000 years for the first time. The geologist Tanguy Racine warns: The ice of smaller caves especially is in danger of disappearing in the near future and with it a valuable climate archive. The study was published in the journal Scientific Reports.

Boosting the single photon rate for quantum communication
A new experiment performed at the University of Innsbruck in collaboration with researchers from Bayreuth, Dortmund, Münster, and Linz allows to double the information transfer rate in future quantum communication systems with the SUPER method.
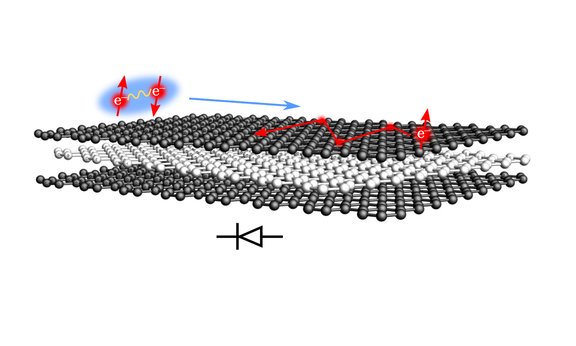
Superconducting diode without magnetic field in multilayer graphene
Superconductors are the key to lossless current flow. However, the realization of superconducting diodes has only recently become an important topic of fundamental research. An international research team involving the theoretical physicist Mathias Scheurer has now succeeded in reaching a milestone: the demonstration of an extremely strong superconducting diode effect in a single two-dimensional superconductor. They report on this in Nature Physics.

Sustainable teaching partnership with Swarovski Waterschool
Since the beginning of July, the UNO-Innsbruck International Summer School, organized by the University of New Orleans, has once again taken place at the University of Innsbruck. For students on the International Management and Communication courses, one of the most successful companies in Tyrol was at the center of teaching for one week: Swarovski and in particular the Swarovski Waterschool - a global educational initiative of the company.

Understanding Climate Research from Caves
The University of Innsbruck Quaternary Research Group recently hosted the international conference "Climate Change The Karst Record IX (KR9)" in Innsbruck and online. Around 200 participants from all over the world attended the conference from 17 to 21 July.

A roadmap for the future of quantum simulation
A roadmap for the future direction of quantum simulation has been set out in Nature this week. An international team of researchers, among them Innsbruck physicists Peter Zoller and Christian Kokail explore near and medium-term possibilities for quantum simulation on analogue and digital platforms.

Reproducibility is the best predictor of generalizability
An international team of researchers was recently able to show that research results from the field of strategic management in some cases generalizes to new time periods and new geographies. The decisive criterion for this is the reproducibility of a study: studies whose results can be obtained again using the same data also tend to generalize to new times and places. They also find that independent scientists are able to forecast which results would be supported in new tests.

Quantum computer works with more than zero and one
For decades computers have been synonymous with binary information – zeros and ones. Now a team at the University of Innsbruck, Austria, realized a quantum computer that breaks out of this paradigm and unlocks additional computational resources, hidden in almost all of today’s quantum devices.

A clear shot into the center of the Milky Way
Nadeen B. Sabha from the University of Innsbruck is the first astrophysicist in Austria to lead a research project at the new James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). Together with an international team, she wants to detect very young stars at the center of our Galaxy. Although the birth of stars near a black hole is very unlikely and requires very special conditions, there is evidence for their existence in the center of the Milky Way.

Invasive fish: Sperm hijacking as success strategy
The Prussian carp is considered one of the most successful invasive fish species in Europe. An international research team led by Dunja Lamatsch from the Research Institute of Limnology, Mondsee, has now described its complete genome for the first time. This provides a much better understanding of the prussian carp's peculiar and efficient reproductive method.
The Hippo and the Hydra
A new study describes the development of the body axis in the immortal freshwater polyp Hydra. It is controlled by the so-called Hippo signaling pathway, which, among other functions, ensures that our organs do not continue to grow indefinitely. The Department of Zoology at the University of Innsbruck was significantly involved in the research and provided important data.
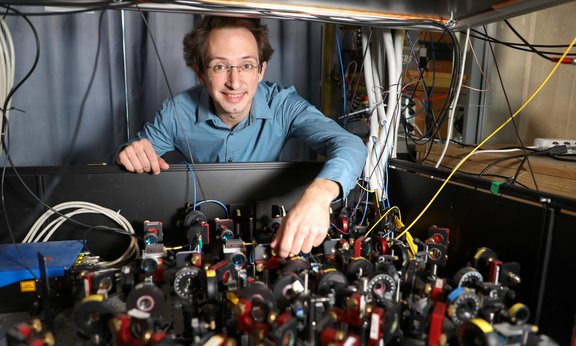
ERC Starting Grant for quantum physicist Martin Ringbauer
Austrian Quantum physicist Martin Ringbauer has been awarded a Starting Grant by the European Research Council (ERC) for his experimental research on new approaches for quantum information processing. The grant, endowed with around 1.5 million euros, is the highest award for successful young scientists in Europe.
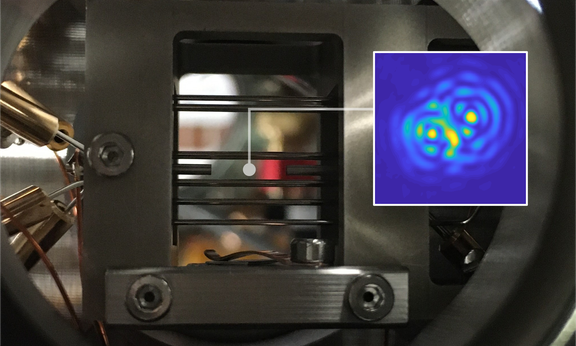
A mirror tracks a tiny particle
Sensing with levitated nanoparticles has so far been limited by the precision of position measurements. Now, researchers at the University of Innsbruck led by Tracy Northup, have demonstrated a new method for optical interferometry in which light scattered by a particle is reflected by a mirror. This opens up new possibilities for using levitated particles as sensors, in particular, in quantum regimes.

Ensuring resilient digital democracy after the pandemic
Together with 13 other universities, the University of Innsbruck has been awarded a €3 million project to research the big question of how Europe's societies can become more resilient after the pandemic. Matthias Kettemann and his team at the Department for Theory and Future of Law will lead a work package on digital communication.
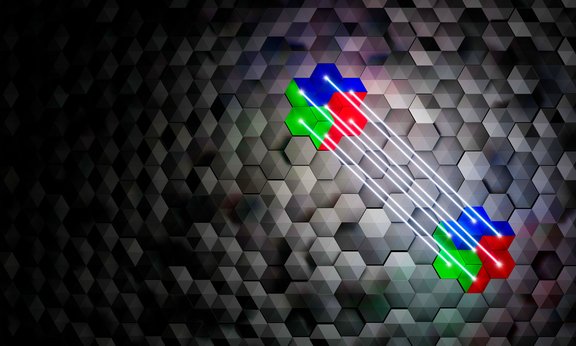
Error-Free Quantum Computing Gets Real
For quantum computers to be useful in practice, errors must be detected and corrected. At the University of Innsbruck, Austria, a team of experimental physicists has now implemented a universal set of computational operations on fault-tolerant quantum bits for the first time, demonstrating how an algorithm can be programmed on a quantum computer so that errors do not spoil the result.

Gutenberg Research Award for Rainer Blatt
This year, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz is awarding its most prestigious research award to Innsbruck quantum physicist Rainer Blatt. He will receive the Gutenberg Research Award 2022 today in Mainz at this year's annual celebration of the Gutenberg Forschungskolleg.
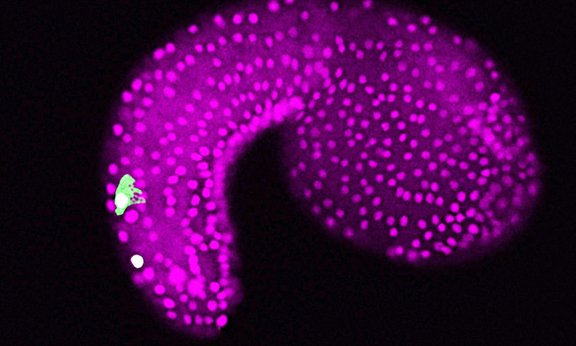
Important genetic origin of our senses identified
Researchers have deciphered the function of a gene that is essential for the formation of neural structures in the head of vertebrates and their perception of the environment. A group of international researchers led by the University of Oxford and including Ute Rothbächer's team at the University of Innsbruck’s Institute of Zoology, published their findings in Nature.
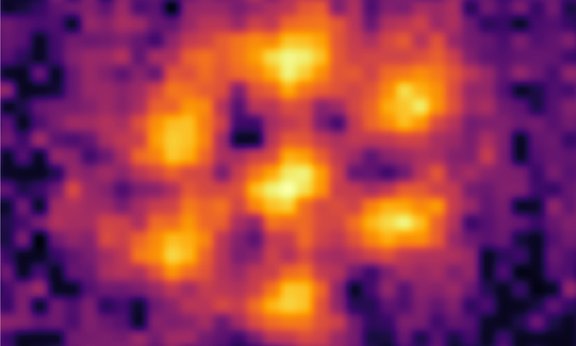
Supersolids go circular 2D
In a new study, investigations led by Francesca Ferlaino and Russell Bisset show how to cool an atomic gas into a supersolid with a circular, 2D shape. The method will allow researchers to further study these exotic states of matter and search for features such as turbulent vortices.

When quantum particles fly like bees
A quantum system consisting of only 51 charged atoms can assume more than two quadrillion different states. Calculating the system's behavior is a piece of cake for a quantum simulator. A research team from the University of Innsbruck and the Technical University of Munich (TUM) has now shown how these systems can be described using equations from the 18th century.

Aurora Universities support partner university in Ukraine
The universities of the Europe-wide Aurora University Network are currently meeting in Innsbruck. The rector of Karasin University Kharkiv is also a guest - she reported on the situation in her city and was presented with 51,000 euros in financial support for her university.

Alpine sustainability at mountain huts: project successfully completed
The Munich Section of the German Alpine Club and the Department of Geography at the University of Innsbruck have successfully completed their project "Alpine Sustainability at Huts - ANAH", which lasted a total of almost two and a half years. This was the first time that the interrelationships of various factors in the management of alpine bases were scientifically investigated with methods for measuring the indicators. The results were presented at a press conference in Munich. Human geographer Jutta Kister is leading the project at the University of Innsbruck.
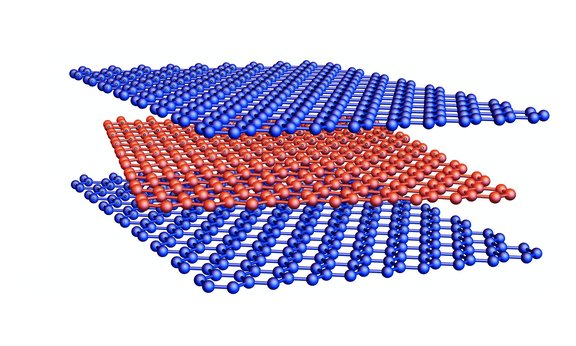
Glimpse inside a graphene sandwich
In the search for novel types of superconductors – phases of matter that that conduct electric current without loss – scientists are investigating materials that consist of multiple layers. A team led by theoretical physicist Mathias Scheurer from the University of Innsbruck, Austria, has studied in detail the properties of a system of three twisted graphene layers and gained important insights into its properties.

Innsbruck researchers awarded three ERC Advanced Grants
University of Innsbruck’s quantum physicists Francesca Ferlaino and Hans Briegel and biochemist Kathrin Thedieck each receive an ERC Advanced Grant, the highest European funding for established scientists in basic research. A total of more than 7 million euros will be invested in basic research in Innsbruck. For Francesca Ferlaino, it is already the third ERC grant after a Starting Grant (2010) and a Consolidator Grant (2016).
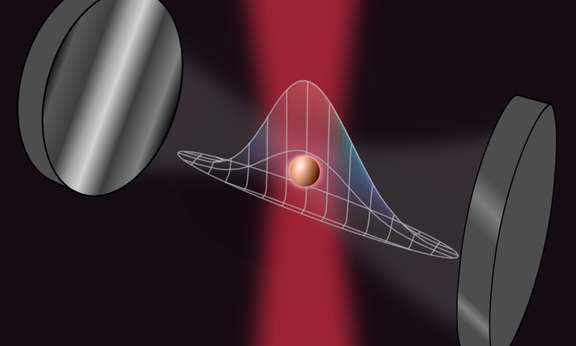
Microcavities as a sensor platform
Sensors are a pillar of the Internet of Things, providing the data to control all sorts of objects. Here, precision is essential, and this is where quantum technologies could make a difference. Researchers in Innsbruck and Zurich are now demonstrating how nanoparticles in tiny optical resonators can be transferred into quantum regime and used as high-precision sensors.

Missing building block for quantum optimization developed
Optimization challenges in logistics or finance are among the first possible applications of quantum machines. Physicists from Innsbruck, Austria, have now developed a method that enables optimization problems to be investigated on quantum hardware that already exists today. For this purpose, they have developed a special quantum gate.

Quantum sensors: Measuring even more precisely
Two teams of physicists led by Peter Zoller and Thomas Monz at the University of Innsbruck, Austria, have designed the first programmable quantum sensor, and tested it in the laboratory. To do so they applied techniques from quantum information processing to a measurement problem. The innovative method promises quantum sensors whose precision reaches close to the limit set by the laws of nature.

VU Amsterdam visit to Innsbruck: Talks about an Aurora Joint Master Program
A delegation of VU Amsterdam recently visited Universität Innsbruck as part of the ongoing activities within the Aurora European University Alliance. Jaap Gordijn, Anna Bon and Hans Akkermans are leading the Pilot Domain „Digital Society and Global Society“, one of the Aurora platforms for educational cooperation, to discuss a potentially new joint master program in this field.

Physicist shed light on the darkness
Experimental physicists led by Gerhard Kirchmair, together with theoretical physicists at the University of Oulu, Finland, have succeeded for the first time in controlling protected quantum states - so-called dark states - in superconducting quantum bits. The entangled states are 500 times more robust and could be used, for example, in quantum simulations. The method could also be used on other technological platforms.

ERC Starting Grant for Mathias Scheurer
Physicist Mathias Scheurer has received an ERC Starting Grant for his research in the field of theoretical quantum many-body physics. Together with the award for Hannes Pichler, this is already the second Starting Grant this year at the University of Innsbruck. The grant, endowed with over 1 million euros, is the most prestigious award for successful young scientists in Europe.

DNA sequencing for newbies and pros
At the University of Innsbruck, a team led by Sebastian Hupfauf from the Department of Microbiology has developed a software package for the simple analysis of DNA sequencing data. The freely available software is intended to allow even beginners to perform such complex analyses. Now the development team has released the third version of the software package.

Hannes Pichler receives ERC Starting Grant
Quantum physicist Hannes Pichler has been awarded a Starting Grant by the European Research Council (ERC) for his theoretical research on quantum many-body physics and quantum information processing. The grant, endowed with around 1.5 million euros, is the highest award for successful young scientists in Europe.

Swaying mountains
Like bridges and tall buildings, large mountains are constantly vibrating, excited by seismic energy form the Earth. An international team of researchers has now been able to measure the resonant swaying of the Matterhorn and make its motion visible using computer simulations. Prof. Jan Beutel from the Department of Computer Science made the highly precise measurements possible.
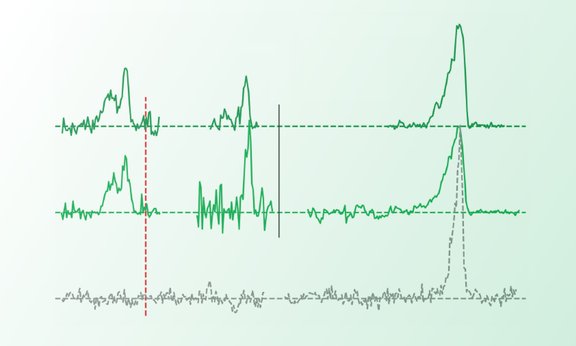
Spectral lines A look inside a molecule
Even the simplest molecular bonds are not fully understood yet. Researchers around the group of physicist Roland Wester from the Institute of Ion Physics and Applied Physics have now studied how negative ions bind to hydrogen molecules – the simplest molecules there are. Together with partners from theory the team has found a precise quantum mechanical description for this process.

Helium bath splash
While working with helium nanodroplets, scientists at the Department of Ion Physics and Applied Physics led by Fabio Zappa and Paul Scheier have come across a surprising phenomenon: When the ultracold droplets hit a hard surface, they behave like drops of water. Ions with which they were previously doped thus remain protected on impact and are not neutralized.
Lanthanoids offer great potential
In a special issue of Nature Physics, Francesca Ferlaino and Matthew Norcia highlight the great potential of ultracold quantum gases from lanthanides. Despite their complexity, they are comparatively easy to access for experimental research and offer a wide range of possibilities for basic research and application.

Rainer Blatt honored
Quantum physicist Rainer Blatt was appointed Distinguished Affiliated Professor of the Technical University of Munich in early November. He was also appointed an external member of the Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics in Garching near Munich this fall. Since spring, Rainer Blatt has been coordinating Munich Quantum Valley, an initiative to expand quantum science in Bavaria.

Collapse of ancient Liangzhu culture caused by climate change
"China's Venice of the Stone Age": The Liangzhu excavation site in eastern China is one of the most significant testimonies of Chinese civilisation. More than 5000 years ago, the city had an elaborate water management system. Massive flooding triggered by anomalously intense monsoon rains caused a sudden collapse, as a team with geologist Christoph Spötl shows in Science Advances.
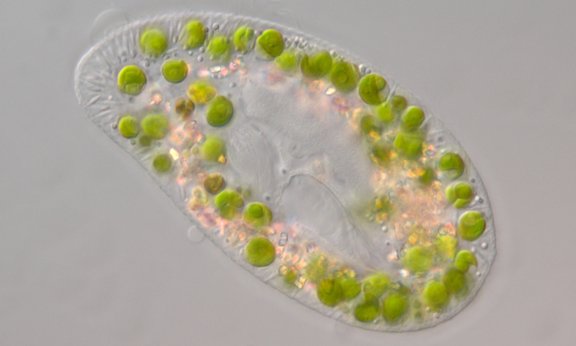
Evolution happens faster than expected
Using a mathematical model, two scientists of the University of Innsbruck and the University of Helsinki were able to determine that in predator-prey dynamics, both sides adapt quickly through evolution.

Studies showcase long-term effects of drought
With the effects of climate change underway, drought is becoming an increasing problem in many parts of the world. Michael Bahn, researcher from the Department of Ecology at the University of Innsbruck, was involved in several studies on the impact of drought on ecosystems. These give insight into the complex processes and highlight the importance of biodiversity in enabling natural systems to resist drought.

A new mechanism protects against cancer cell migration
G3BP proteins inhibit the metabolic driver MTOR, a signaling protein that plays a central role in tumor diseases and developmental disorders of the brain. This is reported in the journal Cell. The study was led by scientists from the University of Innsbruck and the German Cancer Research Center together with the Medical University of Innsbruck and a European network.

Time Travel to a Warm Arctic
An international team of scientists led by Gina Moseley from the Department of Geology at the University of Innsbruck presents the very first analysis of sediments from a cave in northeast Greenland, that cover a time period between about 588,000 to 549,000 years ago. This interval was warmer and wetter than today, the cave deposits provide an outlook in a possible future warmer world.

Top EU Research Award for Roland Wester
Physicist Roland Wester of the University of Innsbruck has been awarded an ERC Advanced Grant. It is the highest funding awarded by the European Research Council. The distinguished scientist and his team will receive up to 2.5 million euros for their research over the next five years.

Non-aggressive behaviour facilitates ant invasion
Under certain circumstances, ant colonies can team up to form huge supercolonies extending across thousands of kilometres and displace native species, if they refrain from aggressive behaviour. A research group from Innsbruck is now investigating how this situation can arise.

We are part of a new European Universities Alliance
On Thursday the European Commission announced the results of the second round of calls for proposals for European Universities Alliances.The University of Innsbruck, which has been active in the Aurora university network since 2019, was able to win the tender despite tough competition with the application for an "Aurora European University" submitted jointly with its partners.

More transparency as a solution against predatory journals
Thousands of predatory journals worldwide present themselves as serious platforms for scientific articles, but they do not offer real quality. Open Peer Review could be a solution.

PNAS Prize for quantum machine learning
A joint research project of physicists led by Hans Briegel and Anton Zeilinger was awarded the 2018 Cozzarelli Prize of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS). In their work, the Austrian researchers present an adaptive computer program that can autonomously design quantum experiments.

Not everything is where it seems to be
Scientists at TU Wien and Innsbruck University have for the first time demonstrated a wave effect that can lead to measurement errors in the optical position estimation of objects. The work now published in Nature Physics could have consequences for optical microscopy, but could also play a role in position measurements using sound, radar, or gravitational waves.
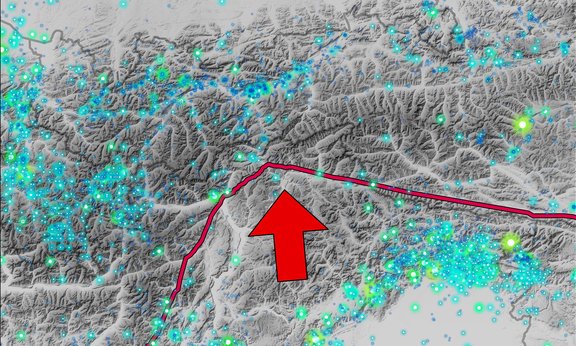
Rumbling Ground
Geologists from the University of Innsbruck used earthquake waves to investigate movements within the eastern Alpine crust. Numerous small, but also large, devastating earthquakes witness that the Alpine orogen has not come to rest.

NOx: Traffic Dramatically Underestimated as Major Polluter
Traffic contributes more to nitrogen oxide emissions in Europe than previously thought. This is the result of a current study carried out by scientists from the University of Innsbruck. The research team headed by Thomas Karl shows that even newer air quality models underestimate traffic related nitrogen oxide pollution by up to a factor of 4.
Stowaways in the Genome
At the University of Innsbruck, scientists have discovered over 30,000 viruses by using the high-performance computer cluster “Leo” and sophisticated detective work. The viruses hide in the DNA of unicellular organisms. In some cases, up to 10% of microbial DNA consists of built-in viruses.

Glacier Loss Day indicates record breaking glacier melt
In the summer of 2022, one of Tyrol's largest glaciers experienced its most significant loss of mass on record. Last year, the Hintereisferner in Tyrol, Austria, reached its Glacier Loss Day (GLD) earlier than ever before. The GLD serves as an indicator of a glacier's health throughout the year, similar to how the Earth Overshoot Day measures Earth's resource consumption. Annelies Voordendag, together with a team of glaciologists at the Department for Atmospheric and Cryospheric Sciences at the University of Innsbruck, employs cutting-edge laser scanning techniques to determine the GLD.

Brisk walks support smoking cessation
Good news for anyone who wants to quit smoking in the new year: In a recently published study, Innsbruck scientists show that ten-minute brisk walking sessions reduce the cravings of temporarily abstinent smokers and improve their overall well-being. The study is the first to compare the effect of indoor and outdoor activity on smoking cessation.
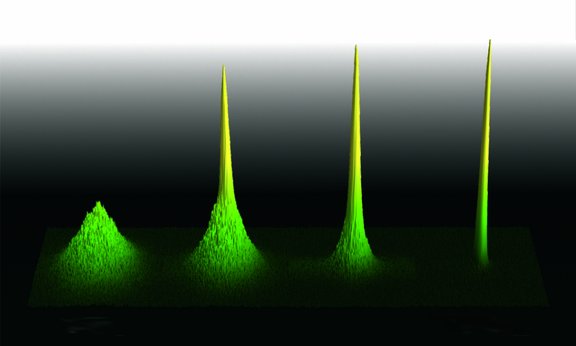
First condensation of non-ground state Cesium atoms
In a pioneering effort, researchers from the University of Innsbruck in collaboration with the University of Durham have for the first time achieved Bose-Einstein condensation of non-ground state cesium atoms. Published in Nature Communications, this research paves the way for new experiments with ultracold atomic gases and the study of many-body quantum physics.

Grand Opening of UNO-Innsbruck Summer School
The UNO-Innsbruck International Summer School officially commenced last Wednesday evening with a Grand Opening Ceremony, heralding the start of an enriching academic and cultural journey for over three hundred students. This prestigious event, featuring more than 30 classes spanning 17 fields of study, was a testament to the collaborative spirit and global reach of the program.

Gletscher in Gefahr: Jedes Zehntelgrad zählt
Ein internationales Forscher*innen-Team mit Beteiligung des Innsbrucker Glaziologen Fabien Maussion beschreibt im Fachmagazin Science mit bisher einzigartiger Genauigkeit das Schicksal aller Gletscher weltweit je nach Temperaturszenarien zwischen +1,5°C und +4°C Erhitzung. Aktuell steuert die Welt in Richtung +3°C, was zum Verlust von 75 Prozent der Gletscher bis 2100 führen würde. Die Forscher*innen appellieren: Jedes Zehntelgrad weniger zählt, um das Abschmelzen einzudämmen.

Anton Zeilinger awarded honorary doctorate
Today, quantum physicist Anton Zeilinger was awarded an honorary doctorate in the Aula auditorium of the University of Innsbruck. The Nobel Prize winner of 2022 was honored for his outstanding scientific achievements. Zeilinger was a professor at the Department of Experimental Physics at the University of Innsbruck from 1990 to 1999, where he carried out much of the work recently honored with the Nobel Prize.
