Teaching ideas
Physical computing in computer science lessons (WS25/26)
As part of the Computer Science Didactics course in the Digital Basic Education and Computer Science teacher study programme, students developed several physical computing projects for use in schools. The aim of the exercise was to design practical learning settings in which programming, hardware and didactic concepts are combined in a meaningful way.
Physical computing offers particular potential for teaching: the interactivity of physical devices increases pupils' motivation , while at the same time encouraging creativity and collaborative teamwork. This makes learning processes more lively, as abstract programming concepts are directly linked to real objects and concrete actions.
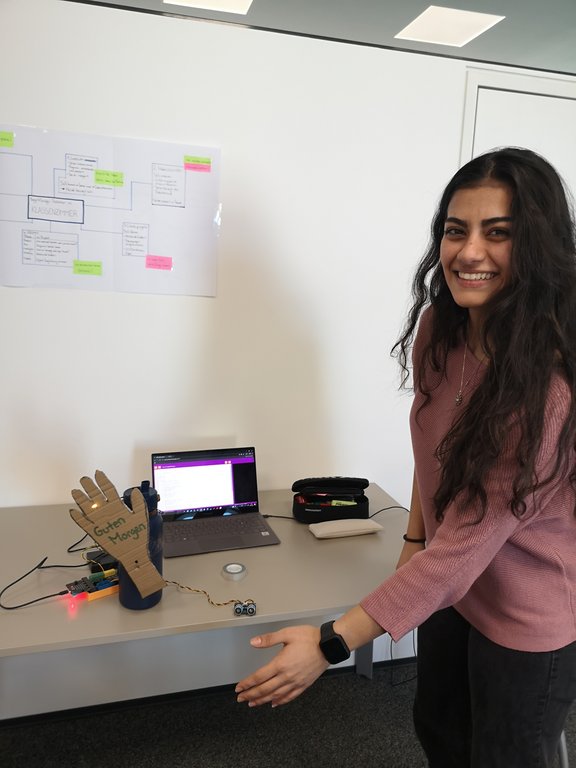
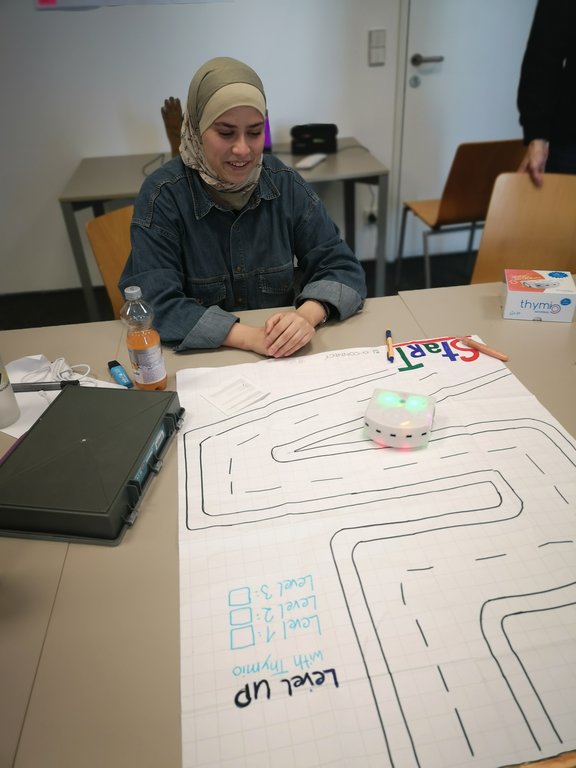
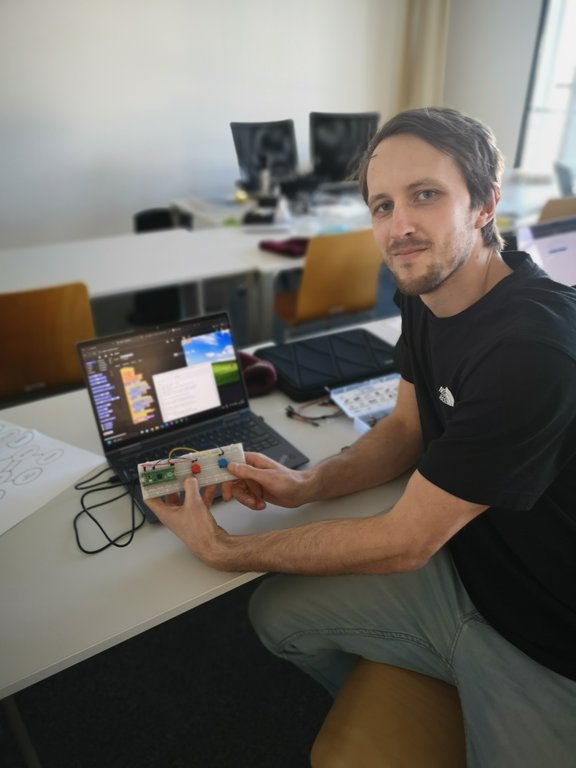
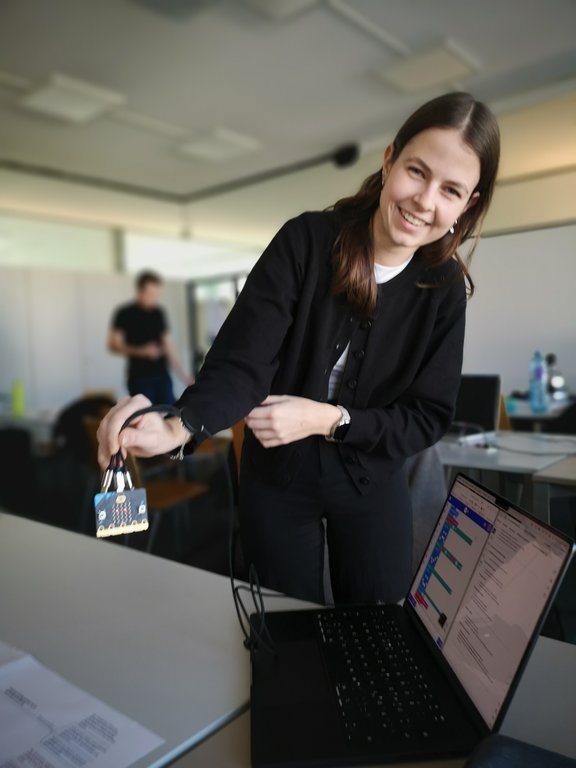
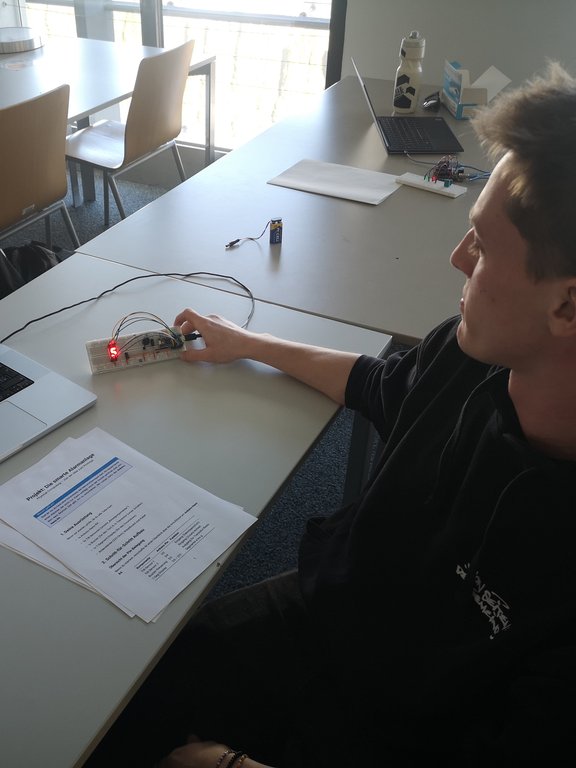
The results are impressive: Both block-based programming environments and script-based programming, for example with Python, were used. These were combined with different hardware platforms such as micro:bit, Arduino and various sensors and actuators.
The projects developed include
- An alarm system with a vibration sensor,
- an automated watering system that uses a water sensor to measure the moisture content of a flower pot and pumps in water as required,
- a noise level light that monitors the background noise in the classroom,
- a welcome robot that waves to arriving pupils via a motion sensor,
- an ambient light to measure the relative humidity,
- a learning brightness traffic light,
- a robotics course,
- a self-built game console controller,
- and many other creative project ideas.
The projects impressively demonstrate how physical computing can contribute to making computer science lessons clear and motivating.
Die Projekte zeigen eindrucksvoll, wie Physical Computing dazu beitragen kann, Informatikunterricht anschaulich und motivierend zu gestalten.
Good-Monkey-Bad-Monkey and Teachable Machine (SoSe 2025)
In the summer semester of 2025, Adrian Hann and Matthias Meusburger implemented several learning stations on the topic of Artificial Intelligence with students of a 9th grade class at the HTL for Construction, Design, and Informatics as part of the proseminar Planning and Implementing Computer Science Instruction. The aim of the teaching units was to convey fundamental concepts of AI and machine learning in an age-appropriate, illustrative, and action-oriented manner.
Adrian Hann employed the two AI Unplugged stations Good-Monkey-Bad-Monkey and Beat the Crocodile, which allowed students to experience key ideas of machine learning in a playful way and without the use of computers. Decision trees were explored using monkey cards, while principles of reinforcement learning were illustrated through reward and punishment in an analogue game. The materials used originate from the AI Unplugged project.
In addition, Matthias Meusburger prepared a further station in which students trained simple AI models themselves using the online tool Teachable Machine. In doing so, they actively engaged with the role of training data and learned how the quality, diversity, and selection of data significantly influence the behavior of an AI system.
Overall, the feedback from the students was very positive. In particular, the playful approach, the opportunity for collaborative group work, and the variation from regular classroom instruction were highly appreciated. The abstract concepts of machine learning, as well as the time-intensive training process—both in the “paper computer” activities and in the digital model training—were perceived as challenging yet motivating.
All materials used within the teaching units can be found at the following link: https://universe.uibk.ac.at/s/42cpStZHNPwkQ8z