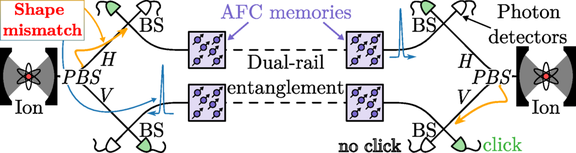
Fig. 1. Proposed architecture to connect cavity-coupled ions with two repeater chains, each producing dual-rail entanglement between extreme rare-earth quantum memories (see text for further definitions and explanations).
Our joint paper presenting an architecture for connecting trapped ions with a quantum repeater based on rare-earth-doped crystal got published. Congratulation to all involved teams!
The paper: Uniting Quantum Processing Nodes of Cavity-Coupled Ions with Rare-Earth Quantum Repeaters Using Single-Photon Pulse Shaping Based on Atomic Frequency Comb, P. Cussenot, B. Grivet, L. Feldmann, S. Wengerowsky, B. P. Lanyon, T. E. Northup, H. de Riedmatten, A. S. Sørensen, and N. Sangouard, Phys. Rev. Lett. 135, 240803, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/hvsx-cx2d
Abstract: We present an architecture for remotely connecting cavity-coupled trapped ions via a quantum repeater based on rare-earth-doped crystals. The main challenge for its realization lies in interfacing these two physical platforms, which produce photons with a typical temporal mismatch of one or two orders of magnitude. To address this, we propose an efficient protocol that enables custom temporal reshaping of single-photon pulses while preserving purity. Our approach is to modify a commonly used memory protocol, called atomic frequency comb, for systems exhibiting inhomogeneous broadening like rare-earth-doped crystals. Pertaining to a growing interest in hybrid quantum information systems designed to exploit the distinct advantages of diverse physical components, our results offer a viable solution for uniting quantum processing nodes with a quantum repeater backbone.
